Comparison of Loop-Free Route Update Algorithms in Multi-Stream, Non-Time-Based Software Defined Networks
Bachelor Thesis Concluding Presentation
Luca Strick
Outline
- (Re-)Introduction of Software Defined Networks
- Algorithms
- Testing Setup
- Results
Introduction
Software Defined Networks (SDN)
Controller decides route for “data flows”
SDN Types:
- Single-flow
- Traffic takes one path from one source to one destination
- Multi-flow/multi-stream
- Traffic takes multiple paths
- Multiple sources and multiple destinations
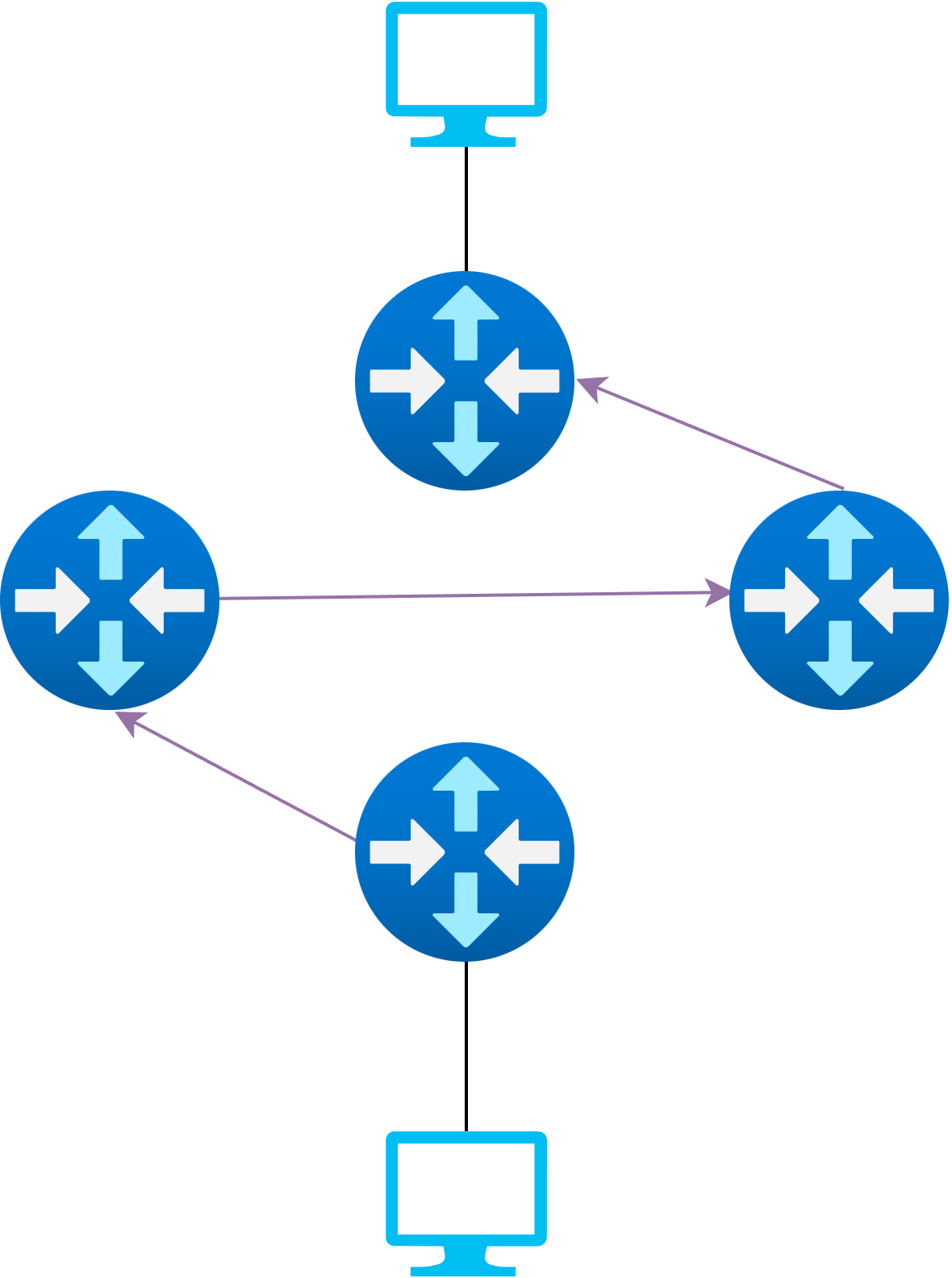
Route Updates
Changing the path of a data flow
Requirements:
- Efficient
- No packet-loss
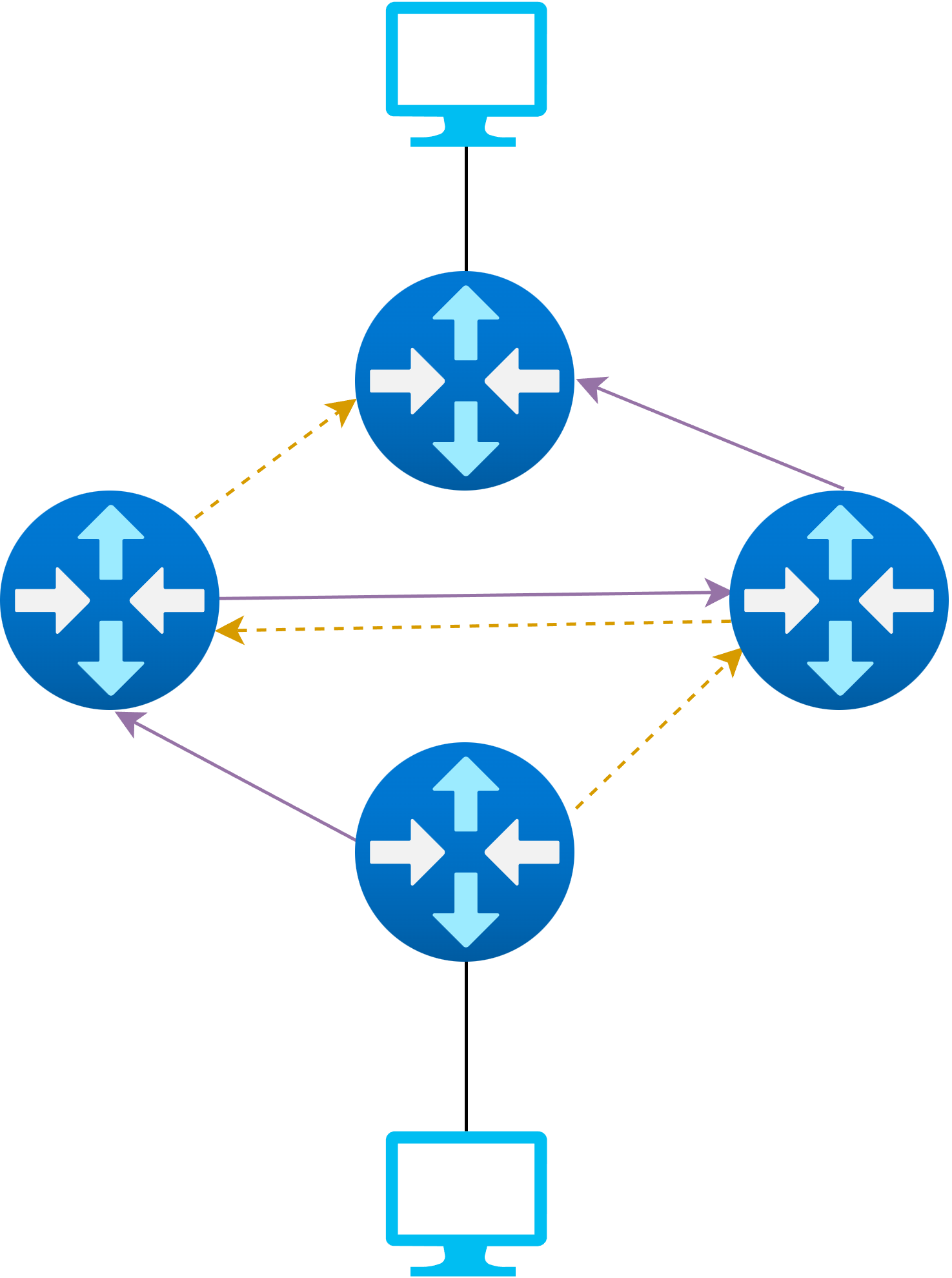
Updating Routes in SDNs
Round-Based Loop-Free
- In rounds that are loop-free, regardless of the order they are applied in during the round
- Next round will only start after all routers have applied the current one
Time-Based
Introduced in Mizrahi and Moses (2016)
Apply all route updates to a buffer
Activate buffer at a set time across all routers simultaneously
Not yet commonly supported on available hardware
Algorithms
Greedy
- Described by Alkhatib (2024)
- Widely known in literature
- Applies all possible steps in each round
- Needs up to \(\Omega(\#_{\mathrm{routers}})\) rounds
(dotted: not yet applied)
Backward
- Described by Mattos et al. (2016)
- Applies routes, starting at the last node
- Always needs \(\#_{\mathrm{routers}}\) rounds
(dotted: not yet applied)
Bruteforce
- Described by Alkhatib (2024)
- Trys all possible variations
- Uses the solution with minimally possible rounds
(dotted: not yet applied)
One-Round
- Developed by Alkhatib (2024)
- Applies all changes in the first round
- “flow swapping”
- not loop-free
(dotted: not yet applied)
Chronicle
- Developed by Zheng et al. (2018)
- Built for Multi-Stream SDNs
- Achieves Congestion-Free schedules
- Needs Time-Based SDNs
- Without congestion: One-Round schedules
(dotted: not yet applied)
Three-Round
- Self-developed
- Always three rounds
- Apply routers with no traffic
- Apply other routers
- Clean-up
- Drops less traffic than One-Round in some cases
(dotted: not yet applied)
Testing Setup
Scope
- Testing and comparing algorithms on real hardware
- Greedy
- Backwards
- Bruteforce
- An algorithm inspired by Chronicle
- One-Round
- Three-Round
- Using multiple sources and multiple destinations
- Investigating characteristics of running a time-based algorithm on non-time-based SDNs
Network Setup
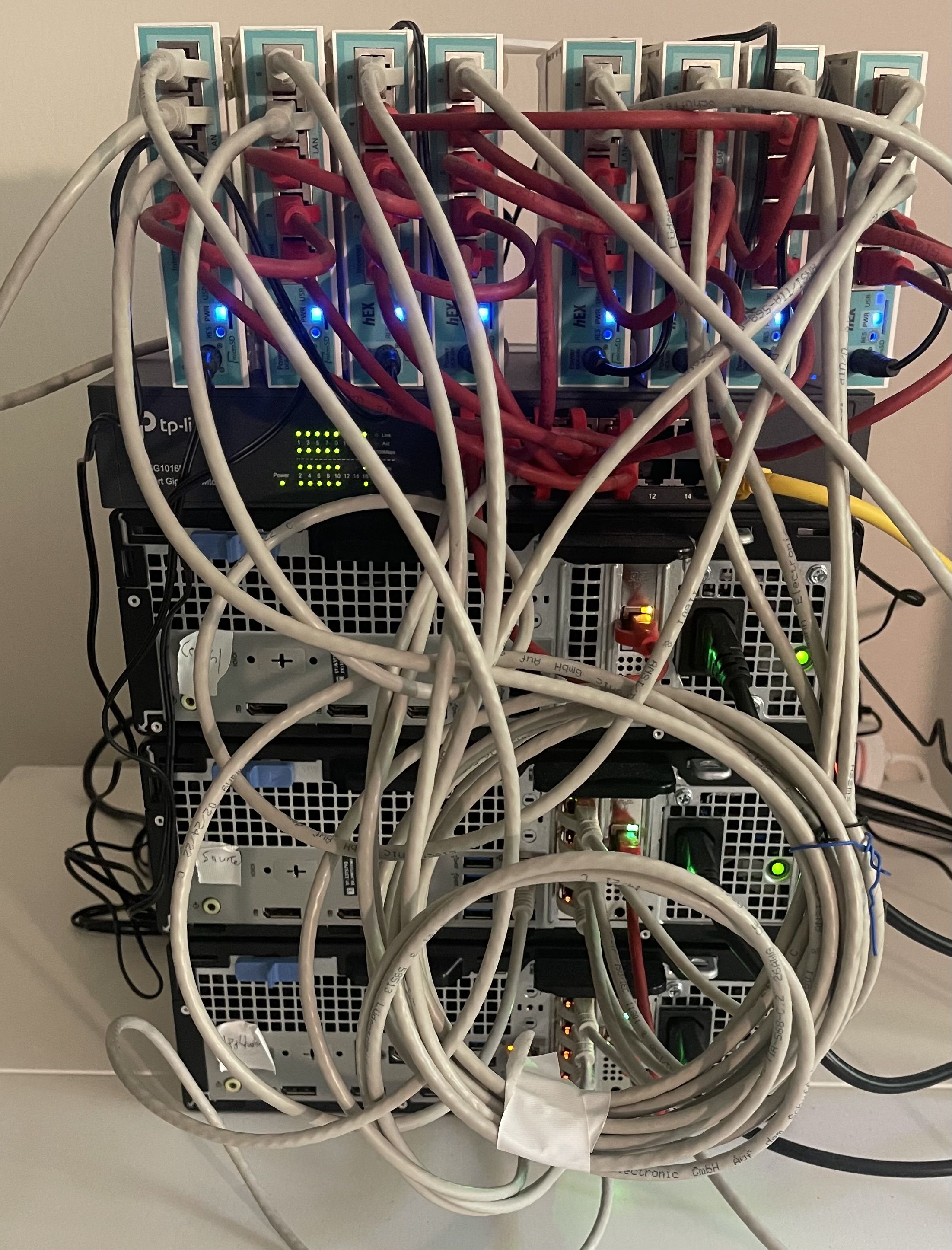
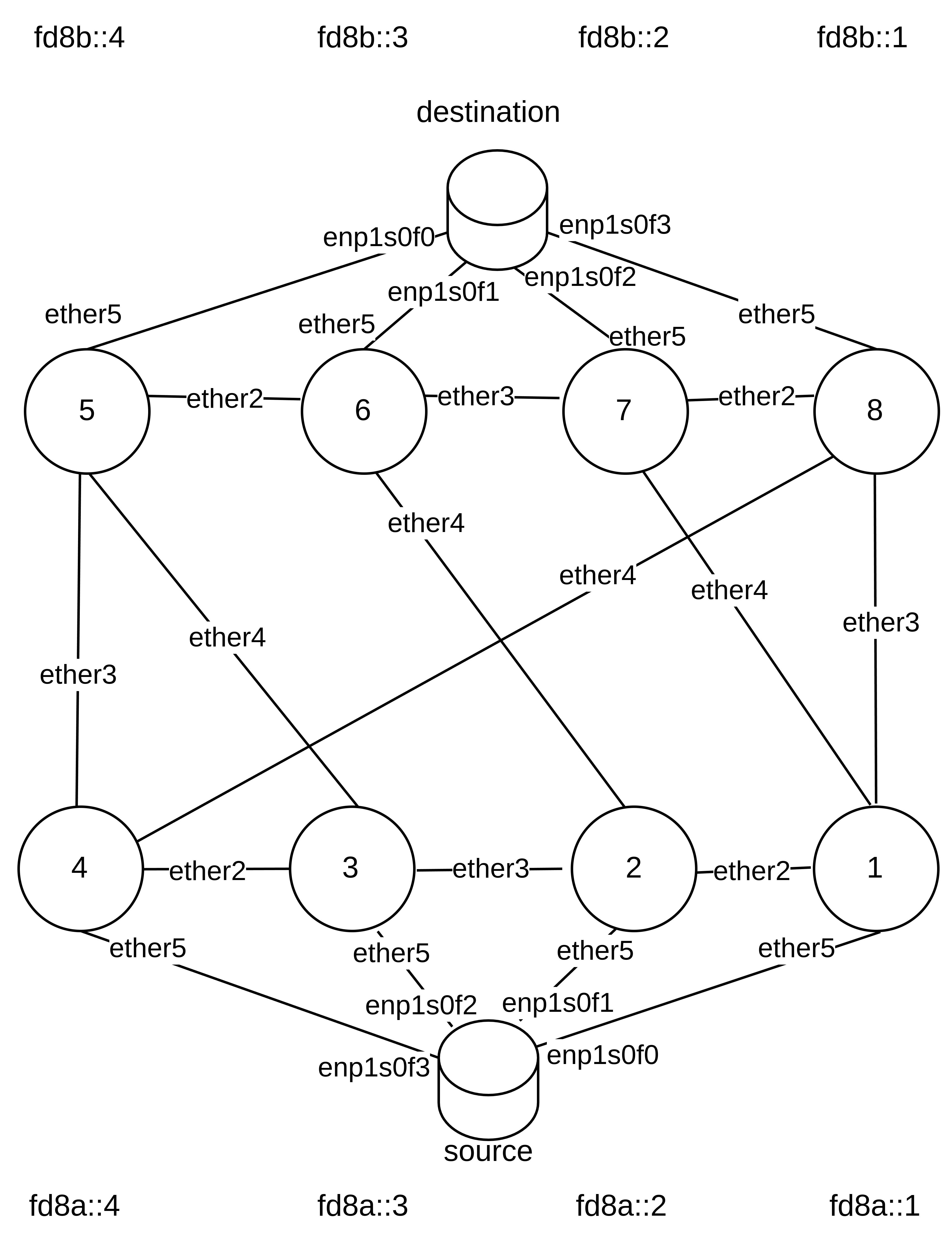

Tools
- MikroTik routers with RouterOS
- Calculation of route updates using Python script and Python package NetworkX
- Custom Go tooling accessing the RouterOS API directly to efficiently apply changes
- Measuring throughput and latency using iperf, additionally measuring with ping and mtr
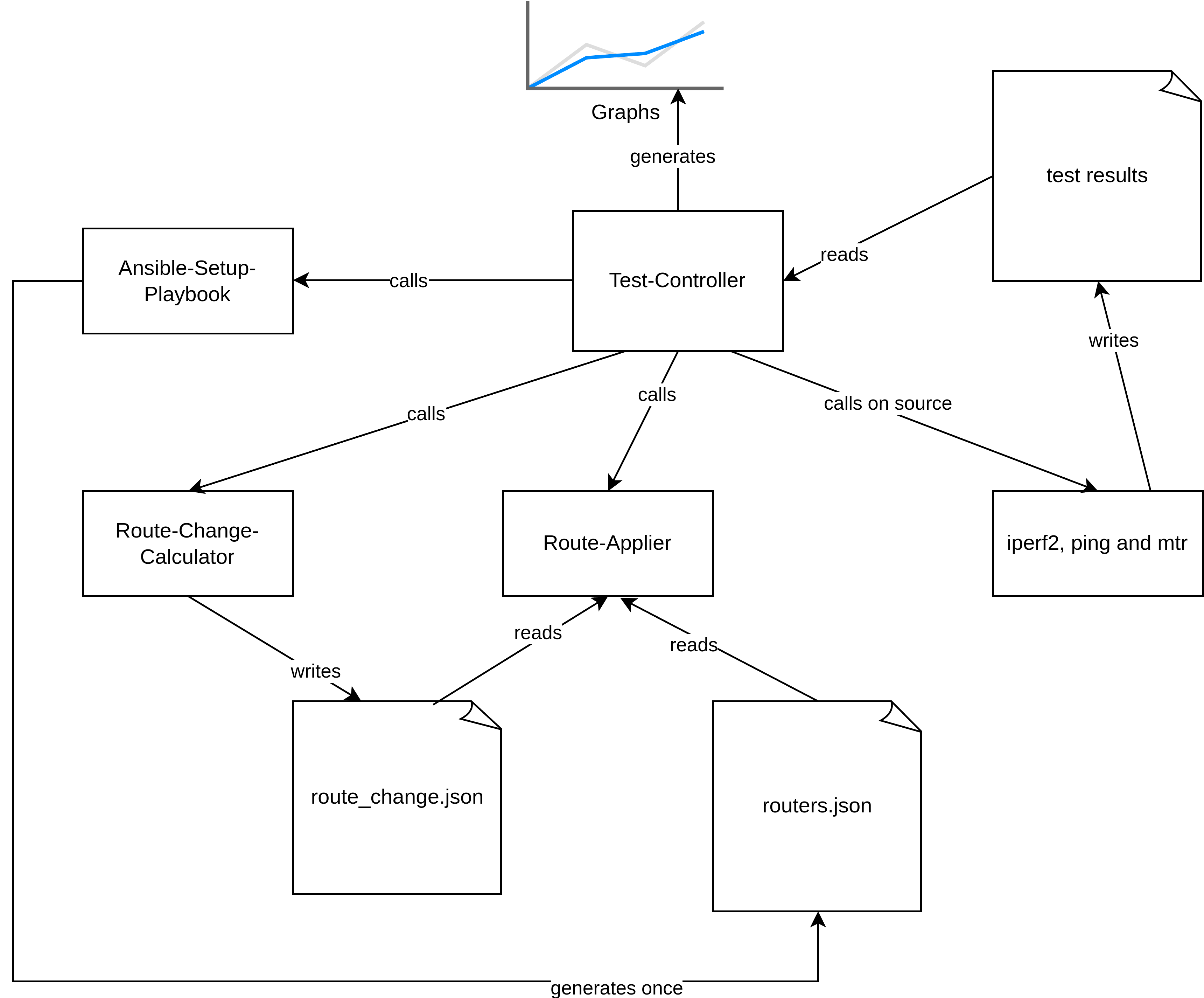
Results
Research Questions
- How can algorithms for loop-free route updates in Software Defined Networks be applied in multi-stream networks?
- Adaptability of single-flow algorithms for multi-stream SDNs
- “On consistent updates in Software Defined Networks”, Mahajan and Wattenhofer (2013)
- Execute algorithm for each flow
- Combine the results into one route change
- How much package loss does adapting time-based algorithms cause for non-time-based Software Defined Networks?
Adapting time-based algorithms
- Calculate round
- Send a script with changes to all routers
- Send command to apply the script file on all routers
Testing procedure



All route changes were executed 100 times for each algorithm
On the topic of efficiency: apply time
On the topic of efficiency: calculation time
On the topic of efficiency: calculation time
On the topic of packet loss
Conflict
Summary
- Software Defined Networks need to update routes quickly and with minimal packet-loss
- Multiple algorithms proposed to allow updating routes in single-flow environments
- Algorithms can be adapted to multi-stream environments without problems
- We evaluated all algorithms in three scenarios with four flows
- Conflict between packet loss and time it takes to apply the changes
- Three-Round creates a middle-ground with moderate packet loss and time requirements
Presentation and sources: ba.lucastrick.eu
Sources
Alkhatib, Mohamed Nour. 2024. “Untersuchung von Automatisiertenkreisfreien Routingupdates Mit Ansible.”
Mahajan, Ratul, and Roger Wattenhofer. 2013. “On Consistent Updates in Software Defined Networks.” In Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks. HotNets-XII. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery. doi:10.1145/2535771.2535791.
Mattos, Ferrazani, Diogo Menezes, Muniz Bandeira Duarte, Otto Carlos, and Guy Pujolle. 2016. “Reverse Update: A Consistent Policy Update Scheme for Software-Defined Networking.” IEEE Communications Letters 20 (5): 886–89. doi:10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2546240.
Mizrahi, Tal, and Yoram Moses. 2016. “Software Defined Networks: It’s about Time.” In IEEE INFOCOM 2016 - the 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, 1–9. doi:10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524418.
Zheng, Jiaqi, Bo Li, Chen Tian, Klaus-Tycho Förster, Stefan Schmid, Guihai Chen, and Jie Wux. 2018. “Scheduling Congestion-Free Updates of Multiple Flows with Chronicle in Timed SDNs.” In 2018 IEEE 38th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), 12–21. doi:10.1109/ICDCS.2018.00012.