Comparison of Loop-Free Route Update Algorithms in Multi-Stream, Non-Time-Based Software Defined Networks
Bachelor Thesis Opening Presentation
Luca Strick
Outline
- Introduction
- Algorithms
- Testing Setup
- Research questions
Introduction
Software Defined Networks (SDN)
Controller decides route for “data flows”
SDN Types:
- Single-flow
- Traffic takes one path from one source to one destination
- Multi-flow/multi-stream
- Traffic takes multiple paths
- Multiple sources and multiple destinations
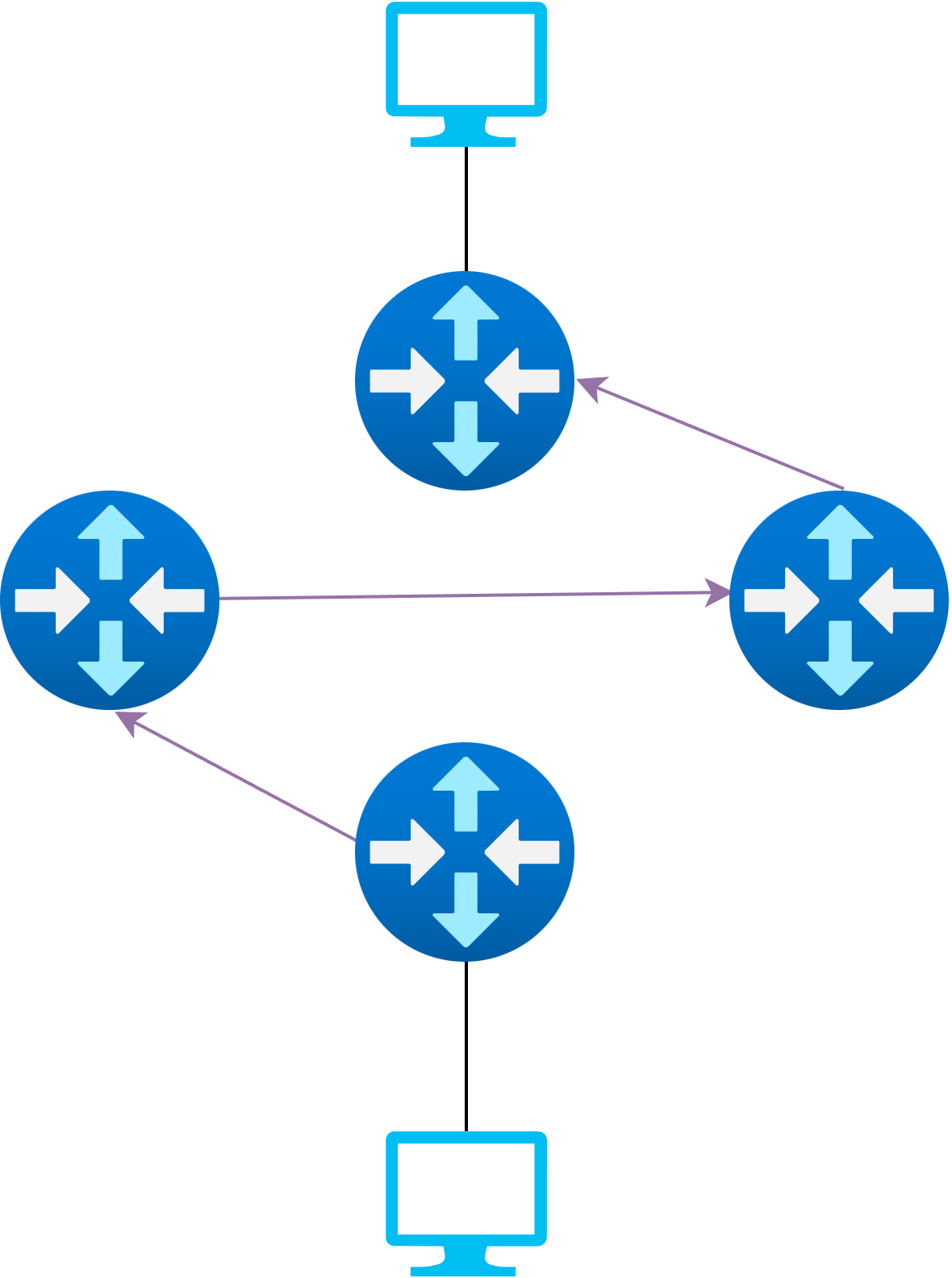
Route Updates
Changing the path of a data flow
Requirements:
- Efficient
- Loop-free
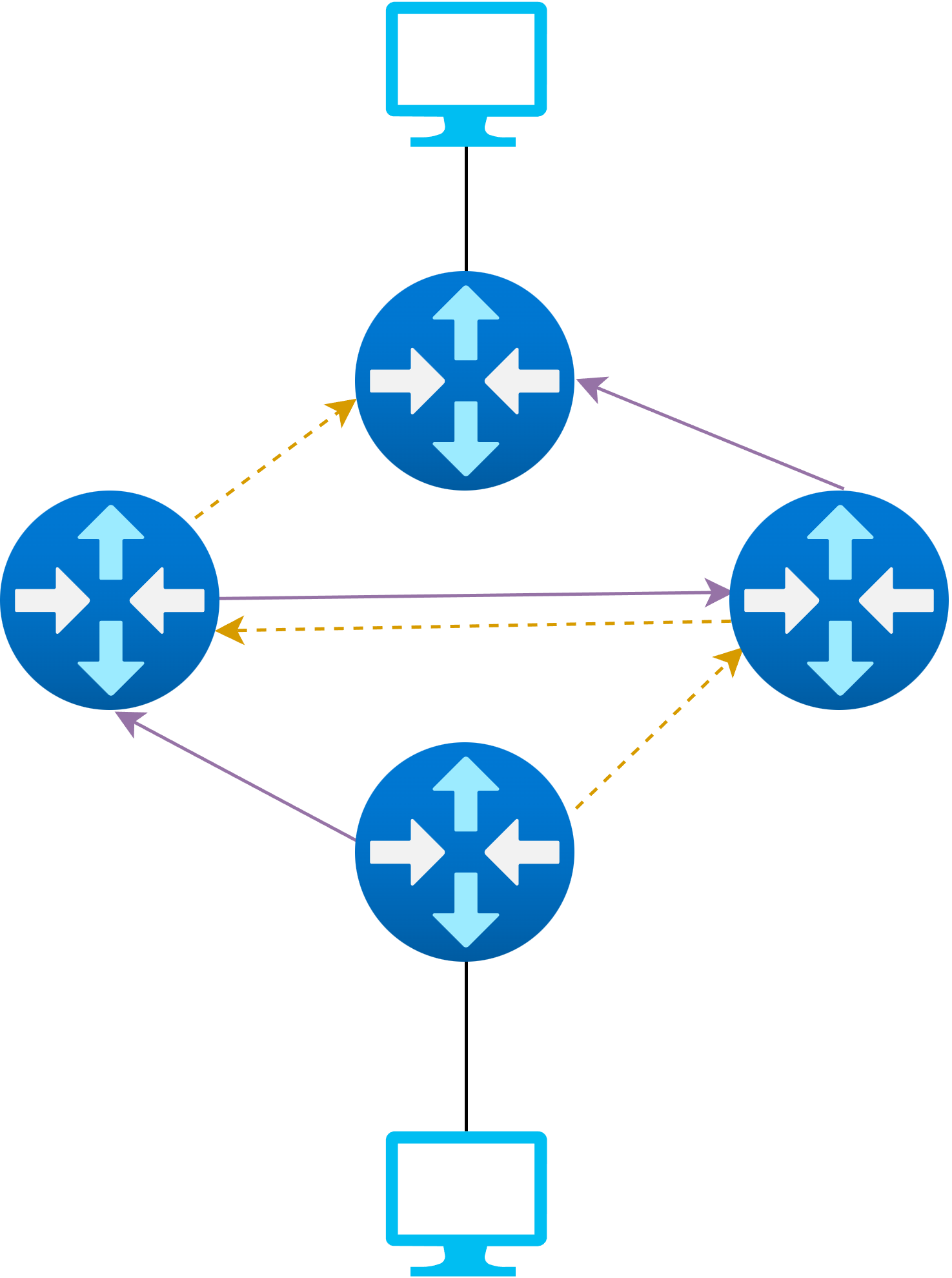
Updating Routes in SDNs
Round-Based
- Apply route changes in rounds that are loop-free, regardless of the order they are applied in during the round
- Next round will only start after all routers have applied the current one
Time-Based
Introduced in Mizrahi and Moses (2016)
Apply all route updates to a buffer
Activate buffer at a set time across all routers simultaneously
Not yet commonly supported on available hardware
Literature
- Algorithms for loop-free route updates in single- and multi-stream SDNs:
- “Loop-Free Route Updates for Software-Defined Networks”, Förster et al. (2018)
- “Congestion-Free Rerouting of Multiple Flows in Timed SDNs”, Zheng et al. (2019)
- Comparisons of multiple algorithms for single-stream SDNs:
- “Untersuchung von automatisierten kreisfreien Routingupdates mit Ansible”, M. N. Alkhatib (2024)
- “Automatisierung und Optimierung von relaxierten kreisfreien Routingupdates mit Ansible”, B. Alkhatib (2024)
- Adaptability of single-flow algorithms for multi-stream SDNs
- “On consistent updates in software defined networks”, Mahajan and Wattenhofer (2013)
Algorithms
Greedy
- Described by M. N. Alkhatib (2024)
- Widely known in literature
- Applies all possible steps in each round
- Needs up to \(\Omega(\#_{\mathrm{routers}})\) rounds
(dotted: not yet applied)
Backwards
- Described by Mattos et al. (2016)
- Applies routes, starting at the last node
- Always needs \(\#_{\mathrm{routers}}\) rounds
(dotted: not yet applied)
Bruteforce
- Described by M. N. Alkhatib (2024)
- Trys all possible variations
- Uses the solution with minimally possible rounds
(dotted: not yet applied)
Chronicle
- Described by Zheng et al. (2018)
- Built for Multi-Stream SDNs
- Achieves Congestion-Free schedules
- Needs Time-Based SDNs
Testing Setup
Scope
- Testing and comparing algorithms on real hardware
- Greedy
- Backwards
- Bruteforce
- An algorithm inspired by Chronicle
- Using multiple sources and multiple destinations
- Investigating characteristics of running a time-based algorithm on non-time-based SDNs
Network Setup
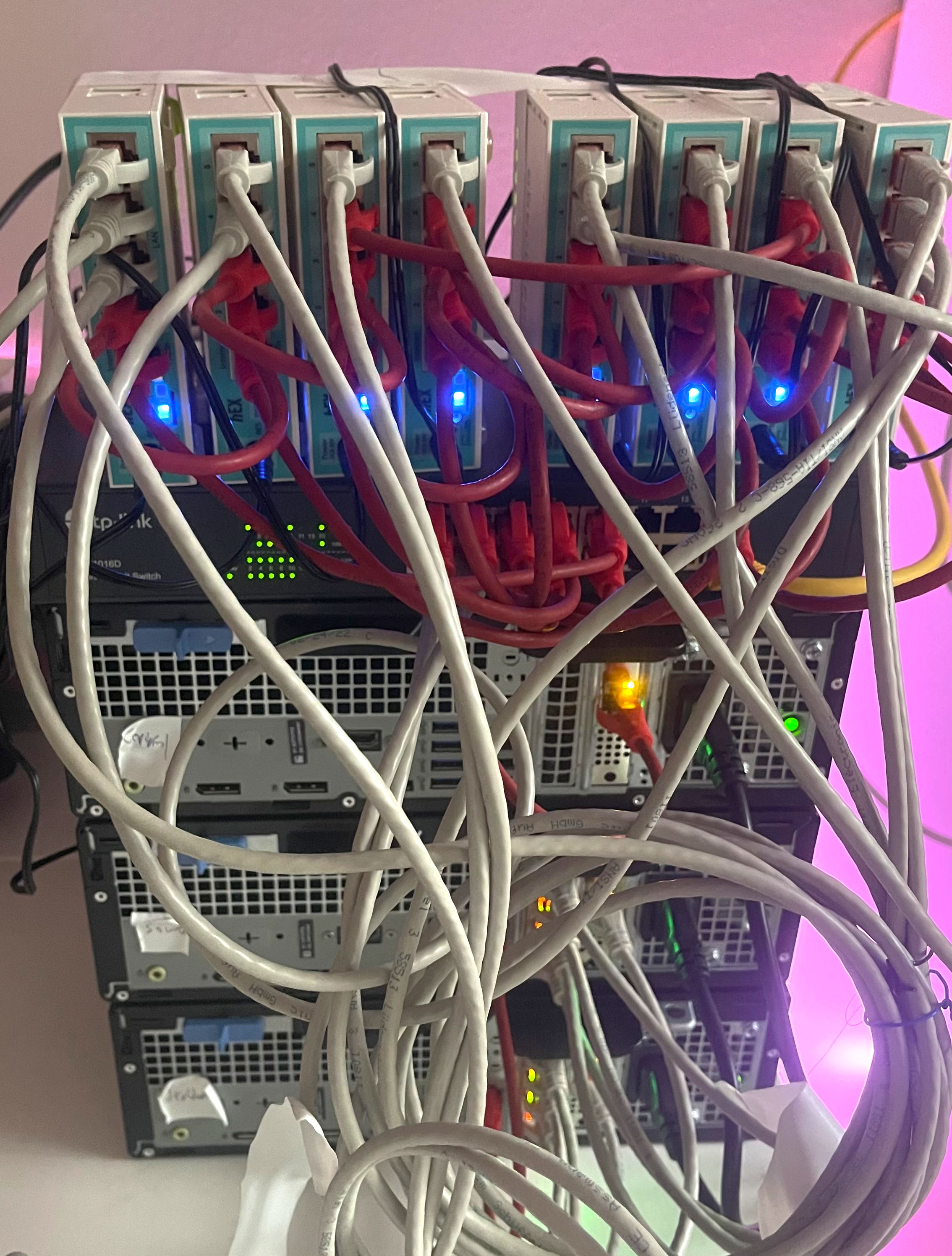
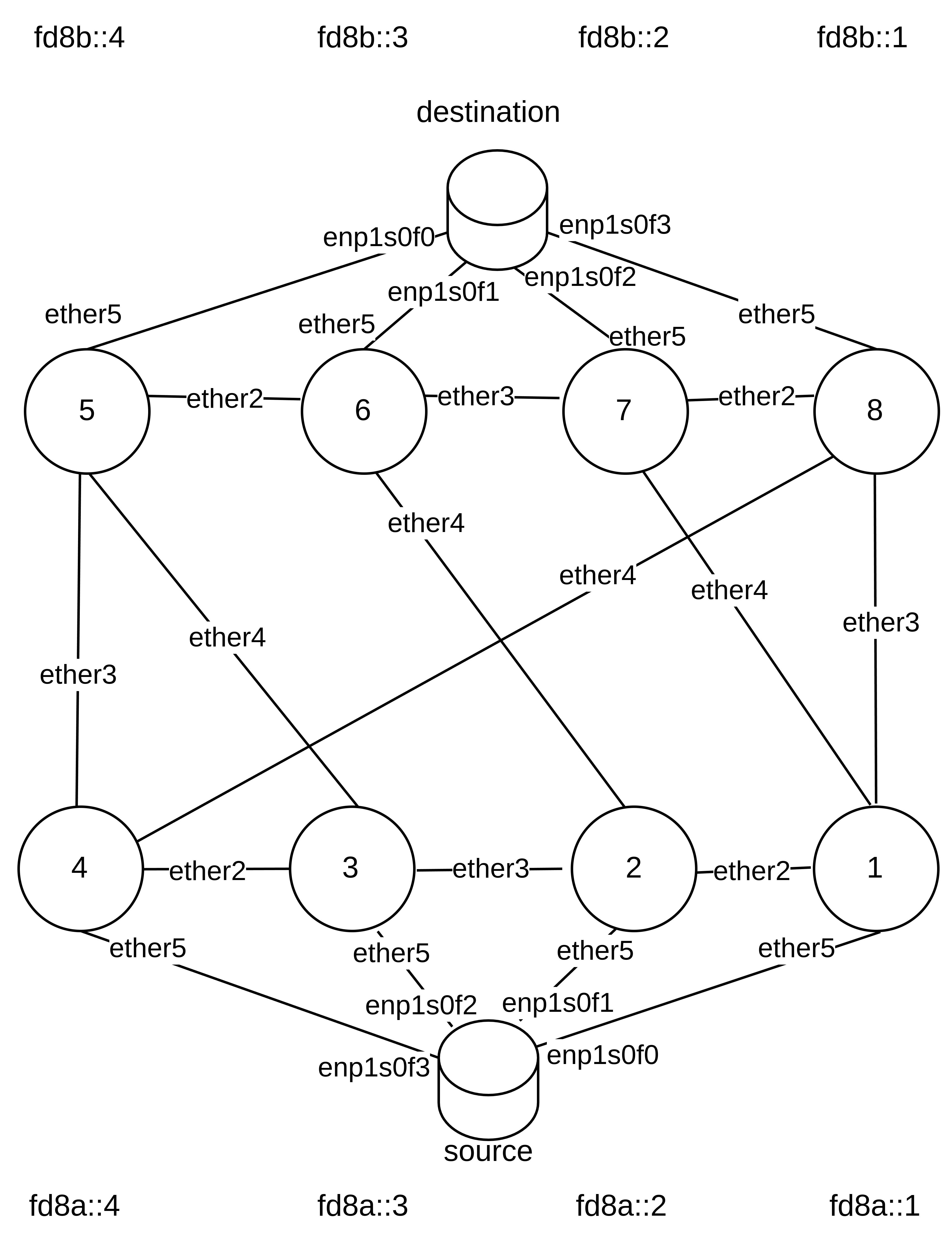

Tools
- MikroTik routers with RouterOS
- Calculation of route updates using Python script and Python package NetworkX
- Custom Golang tooling accessing the RouterOS API directly to efficiently apply changes
- Measuring throughput and latency using iperf, additionally measuring package loss
Research Questions
- How can algorithms for loop-free route updates in software defined networks be applied in multi-stream networks?
- How much package loss does adapting time-based algorithms cause for non-time-based software defined networks?
Summary
- Software Defined Networks need to efficiently update routes without causing loops
- Multiple algorithms proposed to allow updating routes in single-flow environments
- Algorithms can be adapted to multi-stream environments
- One algorithm designed for multi-stream environments
- Uses time-based SDNs
- We will compare four algorithms in the real world using MikroTik Routers
Presentation and sources: ba.lucastrick.eu
Sources
Alkhatib, Bashar. 2024. “Automatisierung Und Optimierung von Relaxierten Kreisfreien Routingupdates Mit Ansible.”
Alkhatib, Mohamed Nour. 2024. “Untersuchung von Automatisiertenkreisfreien Routingupdates Mit Ansible.”
Förster, Klaus-Tycho, Arne Ludwig, Jan Marcinkowski, and Stefan Schmid. 2018. “Loop-Free Route Updates for Software-Defined Networks.” IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 26 (1): 328–41. doi:10.1109/TNET.2017.2778426.
Mahajan, Ratul, and Roger Wattenhofer. 2013. “On Consistent Updates in Software Defined Networks.” In Proceedings of the Twelfth ACM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks. HotNets-XII. New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery. doi:10.1145/2535771.2535791.
Mattos, Ferrazani, Diogo Menezes, Muniz Bandeira Duarte, Otto Carlos, and Guy Pujolle. 2016. “Reverse Update: A Consistent Policy Update Scheme for Software-Defined Networking.” IEEE Communications Letters 20 (5): 886–89. doi:10.1109/LCOMM.2016.2546240.
Mizrahi, Tal, and Yoram Moses. 2016. “Software Defined Networks: It’s about Time.” In IEEE INFOCOM 2016 - the 35th Annual IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, 1–9. doi:10.1109/INFOCOM.2016.7524418.
Zheng, Jiaqi, Bo Li, Chen Tian, Klaus-Tycho Förster, Stefan Schmid, Guihai Chen, Jie Wu, and Rui Li. 2019. “Congestion-Free Rerouting of Multiple Flows in Timed SDNs.” IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 37 (5): 968–81. doi:10.1109/JSAC.2019.2906741.
Zheng, Jiaqi, Bo Li, Chen Tian, Klaus-Tycho Förster, Stefan Schmid, Guihai Chen, and Jie Wux. 2018. “Scheduling Congestion-Free Updates of Multiple Flows with Chronicle in Timed SDNs.” In 2018 IEEE 38th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS), 12–21. doi:10.1109/ICDCS.2018.00012.